Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids at a glance
- Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths in or around a woman’s uterine cavity, thought to be influenced by the hormone estrogen.
- Fibroids may not cause any symptoms, but symptoms can include irregular menstruation, pelvic pain, irregular bleeding, and infertility.
- For some women, fibroids do not require treatment. For other women, treatment may include methods of controlling symptoms or, for more severe fibroids, surgery to remove the growth.
Causes of these fibroids
Although the cause of this fibroid growth in the uterus is unknown, it may be linked to genetics and the hormone estrogen. While a woman continues to have a menstrual cycle, the fibroid will probably continue to grow slowly. The size of fibroids varies greatly, from microscopic growths to large growths weighing several pounds.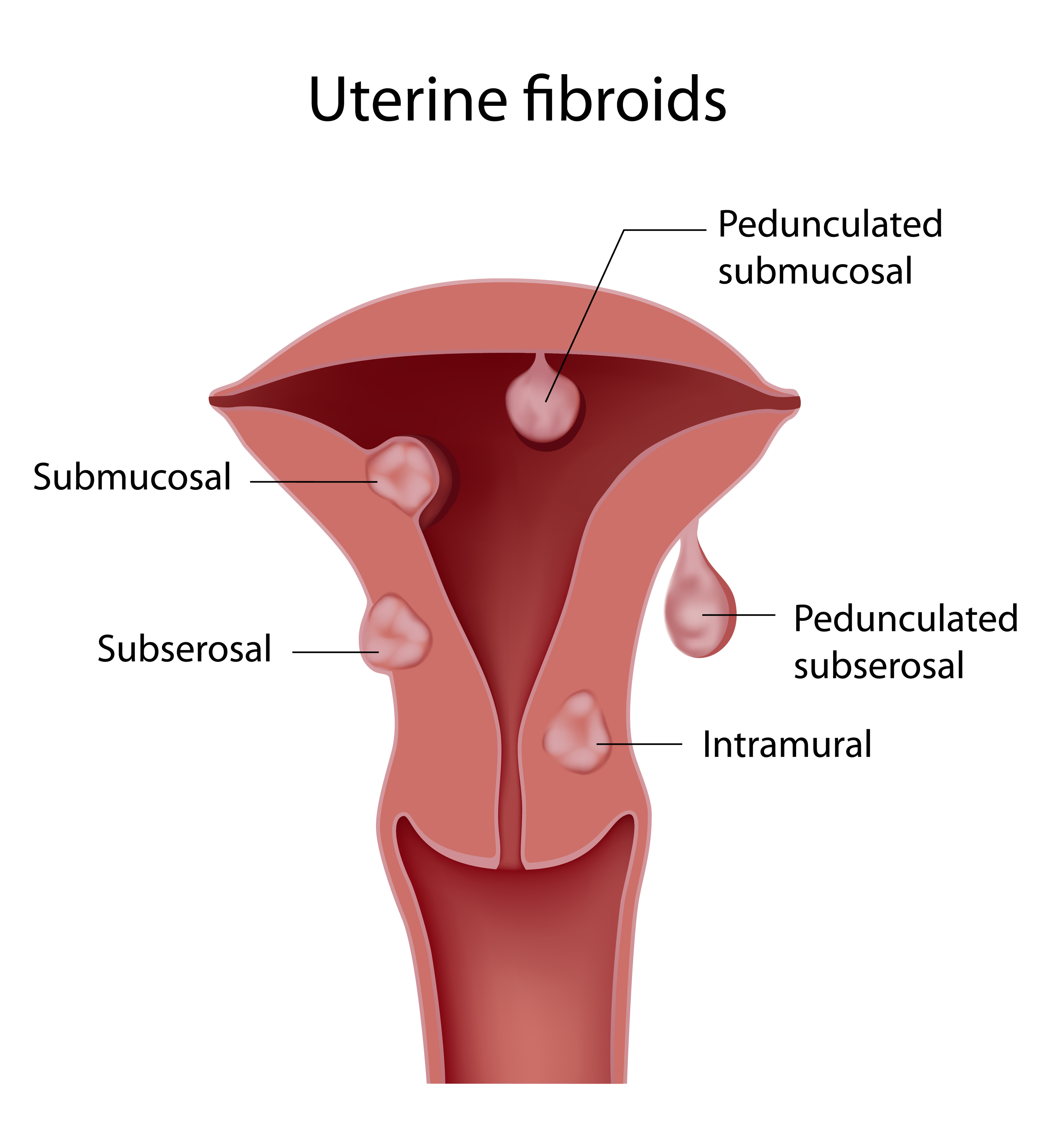
Symptoms of uterine fibroids
Fibroids in the uterus do not always have symptoms. However, common symptoms of uterine fibroids may include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding, sometimes with the passage of blood clots
- Longer than normal menstrual periods
- Pelvic cramping or pain during periods
- Bleeding between periods
- Sensation of fullness or pressure in the lower abdomen
- Need to urinate more frequently
- Pain during sex
Fibroids can develop anywhere in the uterus, and more than one may develop over time. Large fibroids that distort the shape of the uterus or uterine cavity most frequently affect fertility, prohibiting an embryo from implanting.
Experiencing symptoms of uterine fibroids?
Turn to the experts at TRM. We’re here for you.
Request an Appointment
Treatment of uterine fibroids
Some fibroids in the uterus are undetectable during a physical exam, particularly if the woman is overweight, so physicians often diagnose fibroids with ultrasound or MRI. Some women do not need treatment, instead requiring only pelvic exams or periodic ultrasounds to monitor the fibroid’s growth.
Treatment for fibroid symptoms may include:
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs) that release the hormone progestin to help reduce heavy bleeding and pain
- Short-term hormonal therapy injections to help shrink the fibroids
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naprosyn for cramps or pain
- Iron supplements to prevent or treat anemia due to heavy periods
- Birth control pills (oral contraceptives) to help control heavy periods
If a fibroid is affecting the woman’s health or fertility, surgical removal may remedy the problem. If a fibroid needs to be removed, there are several surgical procedures that can be performed:
- Women who have fibroids growing inside the uterine cavity can have their fibroids removed in an outpatient procedure using a hysteroscope
- Myomectomy surgery completely removes the fibroids and preserves the woman’s ability to become pregnant. However, there is a risk that more fibroids may develop following surgery.
- Another procedure called embolization cuts off the blood supply to the fibroid, causing it to shrink and die. However, this procedure is not advisable for women who wish to become pregnant in the future.
- Hysterectomy removes the woman’s reproductive system completely – removing the fibroids and virtually eliminating the possibility for more to grow. This option makes it impossible for a woman to become pregnant and affects the balance of hormones, so it should be a last resort if all other options have failed.

